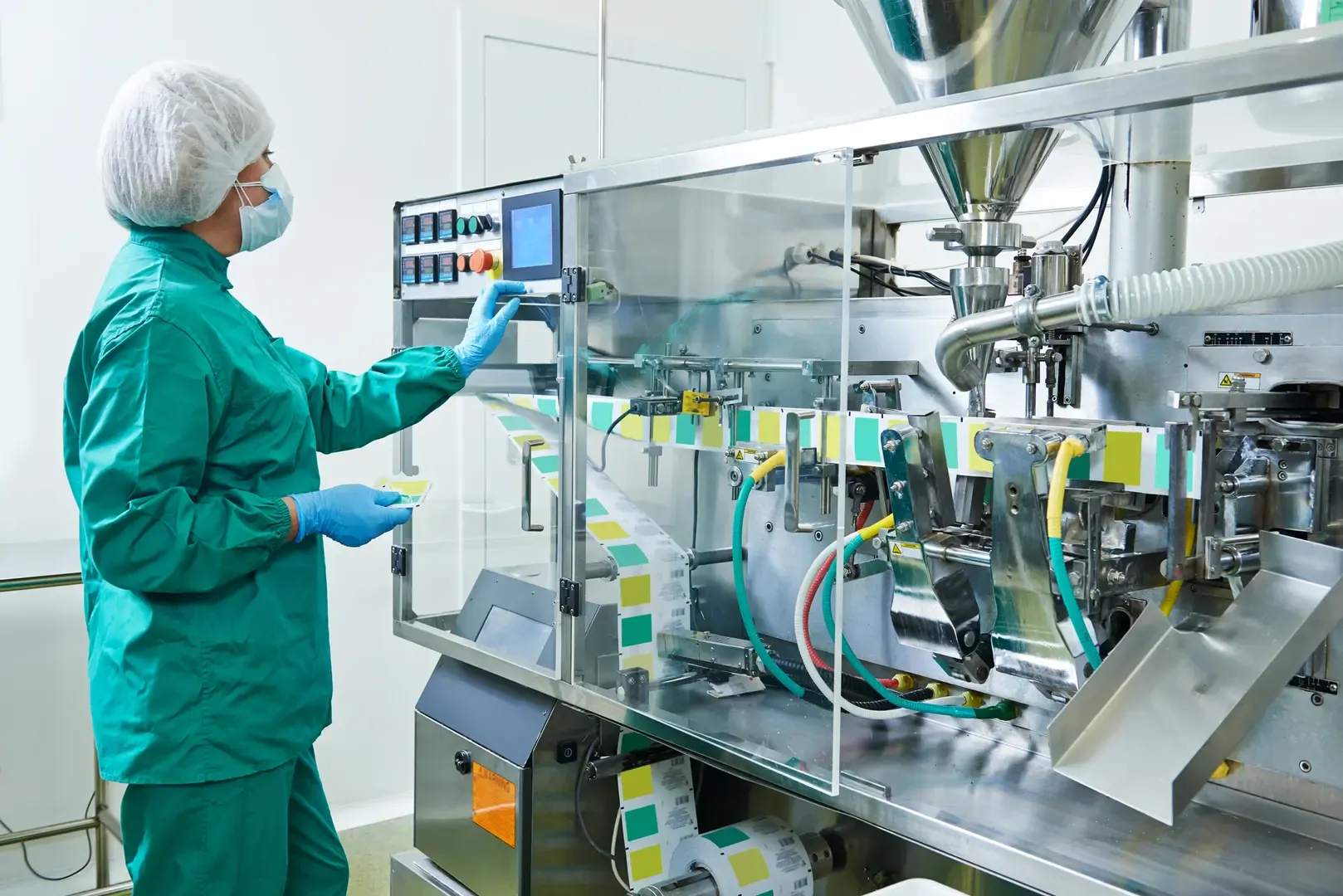
2D Vision Systems
A 2D machine vision system is a powerful technology used in various industries for automating visual inspection and quality control processes. It involves the use of cameras, sensors, and image processing software to capture and analyze 2D images or patterns. These various vision systems tools and systems play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, control assurance and efficiency of manufacturing processes.

What exactly are these 2D vision systems and machine vision systems? In simple terms, vision systems are smart visual systems that replicate human vision capabilities with exceptional accuracy and speed. By utilizing advanced algorithms and computer vision techniques, 2D and machine vision systems can quickly and precisely inspect and identify defects, measure dimensions, read barcodes, verify text, and perform many more crucial tasks.
This technology is widely employed across various manufacturing, such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food and beverage, as a solution to enhance productivity, reduce errors, and improve product quality.

Applications of 2D Vision Systems in Manufacturing
Seamless and efficient manufacturing process
These intelligent systems utilize smart cameras, sensors, and advanced image processing to analyze 2D images, creating a seamless and efficient manufacturing process. Picture a real-time operation on production and assembly line scan, where defects are identified with lightning speed, preventing faulty products from reaching customers and optimizing overall production.
Streamlining the packaging process
But the impact doesn't stop there. 2D machine system play a pivotal role in the supply chain, particularly in streamlining the packaging process and barcode. This revolutionary technology isn't just about improving the packaging process and inspection of packaging; it's about reshaping industries and driving excellence in every step of the manufacturing journey.
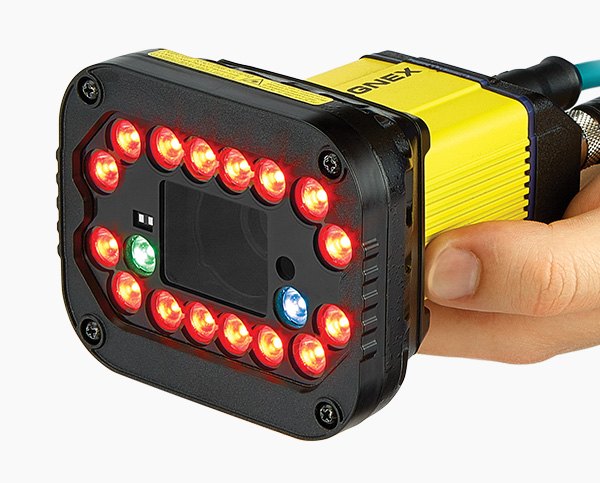

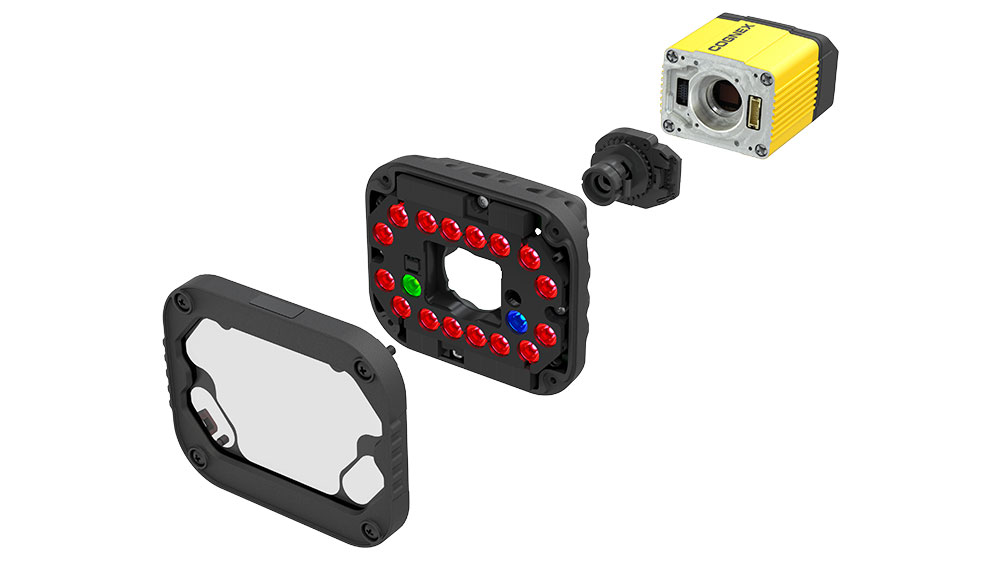
Components of a 2D Vision System
A 2D machine vision system consists of various essential components that work together to capture and process images and data for inspection and analysis. Understanding these components is crucial for selecting and configuring the right, smart camera system for specific application requirements.
2D Machine Vision: High-Resolution Cameras
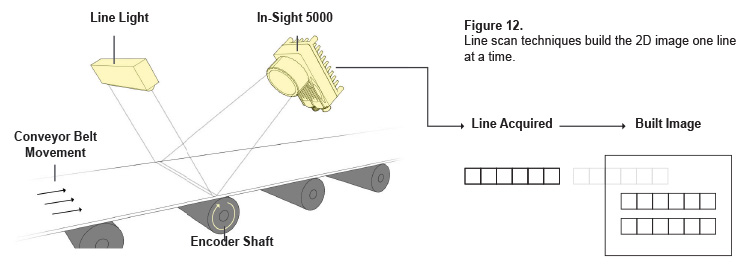
One of the primary components of a 2D vision machine system is the camera. In a 2D machine system, the camera plays a vital role, employing high-resolution cameras with advanced sensors for capturing high-precision images for verification of inspected products such as defective products. Those quality assurance systems have the ability for codes identification such as barcode. This vision tool is perfect for automation, monitoring, traceability of labels, and codes identification.
The camera type, be it area scan or line scan, is chosen based on tolerance of factors like image quality, field of view, and the required speed for tasks like line scan, verification of image and shape analysis, and line scan for ensuring high accuracy.

Lighting Techniques
Lighting techniques also play a critical role in 2D vision systems. Proper lighting is essential to ensure optimal image and create inspection and measurement results of read barcodes and labels. Different lighting techniques, such as direct lighting, front light, backlighting, or diffused lighting, can be employed based on the specific light requirements of the object, form and the inspection or measurement task.
Image Processing Software
Moreover, image processing software forms a vital component of a 2D vision. This software analyzes the captured images, applies algorithms for defect label detection, pattern recognition, barcode reader, bin picking and other inspection tasks. Vision systems allows for high precision, customization and configuration of various parameters to suit the specific needs and ease of use and ease of use of the application.
Choosing the Ideal 2D Vision System for Enhanced Manufacturing
By understanding about light, the role of light, and characteristics of light in each component, businesses can effectively design and implement a 2D vision and light that meets their control objectives and enhances their manufacturing processes.
Choosing the Right 2D Vision System
Selecting the right 2D barcode reader is crucial to the ability to both ensure quality, measurement data and efficient inspection for specific manufacturing requirements such as label codes. There are various factors that businesses should consider before making a decision.
One of the key factors is understanding the specific application needs. Different industries and products require different types of inspections and measurements. Identifying the inspection tasks, desired accuracy, and speed requirements will help determine the suitable features and capabilities to look for in a barcode reader.
Evaluating the capabilities and performance of different 2D vision system
It is crucial to assess their track record, experience, and expertise in the industry regulations providing reliable services and industry-specific, services and solutions. Reading customer reviews and case studies can provide valuable insights into the supplier's reliability, traceability and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, compatibility and installation with existing production assembly lines should be considered. Ensuring that the 2D vision can seamlessly integrate with the in line and existing in line data and infrastructure and communicate effectively with other systems will help streamline the implementation and assembly line up process.
In summary, carefully analyzing application needs, supplier capabilities, and installation requirements are essential steps in choosing the right 2D vision solution that aligns with a company or supply chain's manufacturing objectives and quality goals.

Integrating a 2D Vision System in supply chain
Integrating a 2D vision inspection system into existing manufacturing processes requires careful planning, monitoring and consideration. Effective installation ensures that the system seamlessly works alongside other production line components and maximizes its potential and ability to enhance quality and efficiency.
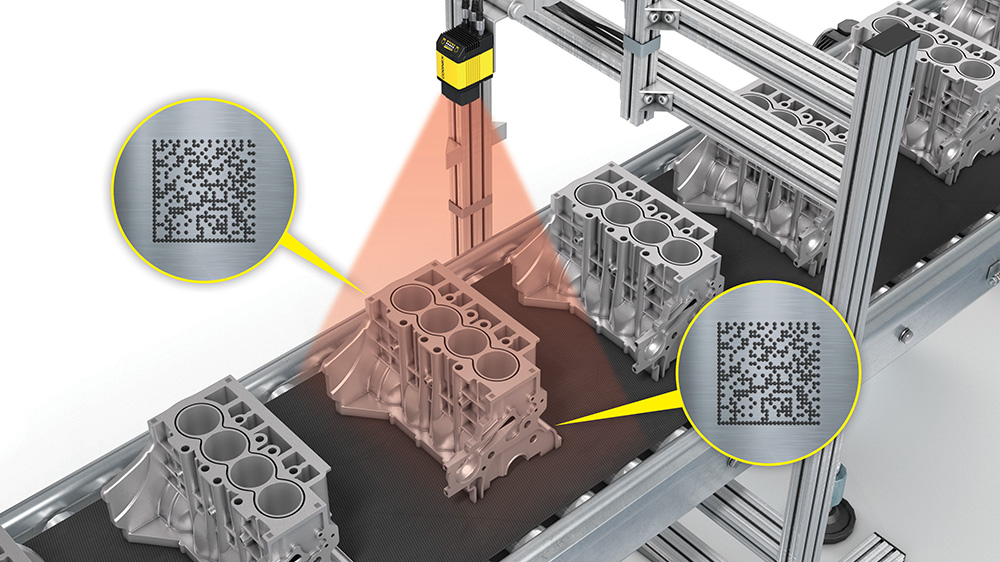
One of the key factors in installation is understanding how the 2D vision will connect with existing production line equipment. This includes establishing communication protocols, such as Ethernet or serial connections, to enable data transfer between the vision monitoring and other devices, such as PLCs or industrial robots itself. Ensuring compatibility and interoperability is crucial for a smooth integration process.
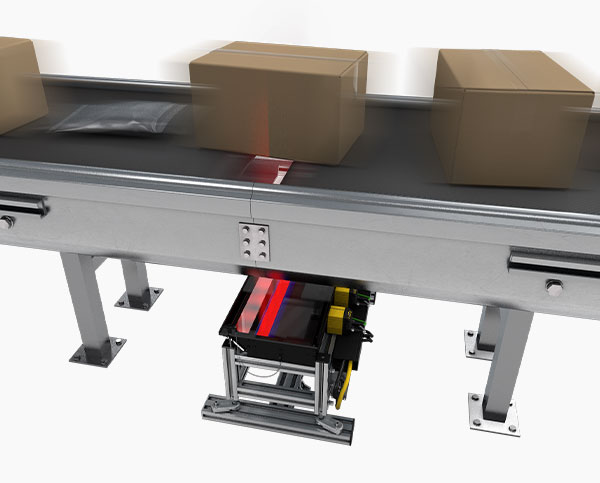

Calibration smart camera position, and alignment are critical steps in achieving accurate and reliable inspection results. Proper calibration of camera angles, lighting, and vision components ensures optimal image capture and analysis of label, barcode and other. Additionally, aligning the system with the production line, considering factors like conveyor speeds and product positioning, helps achieve consistent and reliable color image take, inspection accuracy and performance.
Another key aspect of integration is training operators to effectively use and maintain the 2D vision. Providing comprehensive training on system operation, troubleshooting, and routine maintenance empowers employees to utilize the system's capabilities to their fullest extent. Vision systems also helps in early detection of potential issues, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity. Those vision tools are great to verify and inspect defects form and other errors.
Advancements in 2D machine vision system technology
Learning algorithms
One significant advancement is the integration of machine vision software and learning algorithms in 2D machine vision software systems. Machine learning enables 2d machine vision systems to learn from large datasets and improve their accuracy over time.
This allows for more intelligent and adaptive inspection processes, enhancing defect detection and reducing false positives or negatives. Microscan offers a number of products for package inspection, including smart cameras, vision software, and 2D imagers with OCR decoding capability.

Higher precision and efficiency
Industry end user-specific advancements in 2D vision systems are gaining prominence, as manufacturers seek tailored solutions to meet their unique needs.
From specific algorithms designed for automotive part inspections to enhanced barcode label reading capabilities for medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging, these advancements cater our vision tools to industry end user-specific requirements and deliver higher precision and efficiency.
A comprehensive analysis
Furthermore, the emergence of 3D vision technologies and the fusion of 3D and 2D capabilities have expanded the scope of vision tools and tolerance range of label and barcode inspection possibilities.
Combining depth information with 2D images allows a determined and comprehensive analysis, enabling accurate measurements, volume calculations, and identifying surface defects more effectively such as verify and inspect barcode.
Pattern recognition
Pattern recognition succes In addition to its crucial role in image processing, pattern recognition significantly enhances the accuracy and efficiency of defect detection and quality control in industrial applications. By identifying consistent patterns and anomalies, this technology ensures that even the smallest defects are detected and addressed promptly. This leads to improved product quality, reduced waste, and increased operational efficiency.

Overcoming Challenges in Implementing 2D machine vision systems
Implementing 2D vision systems can come with certain challenges that businesses need to address for successful deployment. Understanding and finding solutions to these challenges is crucial to ensure optimal performance and maximize the benefits of those machine vision systems.
One common challenge is the complexity of integration. Properly integrating a 2D machine vision into existing production lines requires coordination between different departments, such as engineering, IT, and operations. It is essential to establish clear communication channels, set realistic timelines, and assign dedicated resources to address any integration-related hurdles.
Training operators for the effective use of the 2D machine vision is another key challenge. Operators need to be trained on system operation, software interfaces, and troubleshooting procedures. Providing comprehensive training programs and refresher courses can help operators gain competency and confidence in utilizing the machine vision to its full potential.
Maintenance and troubleshooting can also pose challenges. Regular maintenance is crucial to keep the system in optimal condition and minimize any potential downtime. Businesses should establish preventive maintenance schedules and provide proper documentation to address common issues and troubleshoot any unexpected problems efficiently to let the machine inspect and verify barcode.
By proactively identifying and addressing these challenges, businesses can successfully implement 2D machine vision systems, improve their processes, and achieve long-term operational excellence.
